Lumbago - Ischialia
Sciatica is back pain and can be caused by a variety of causes, which are diseases of the spine.
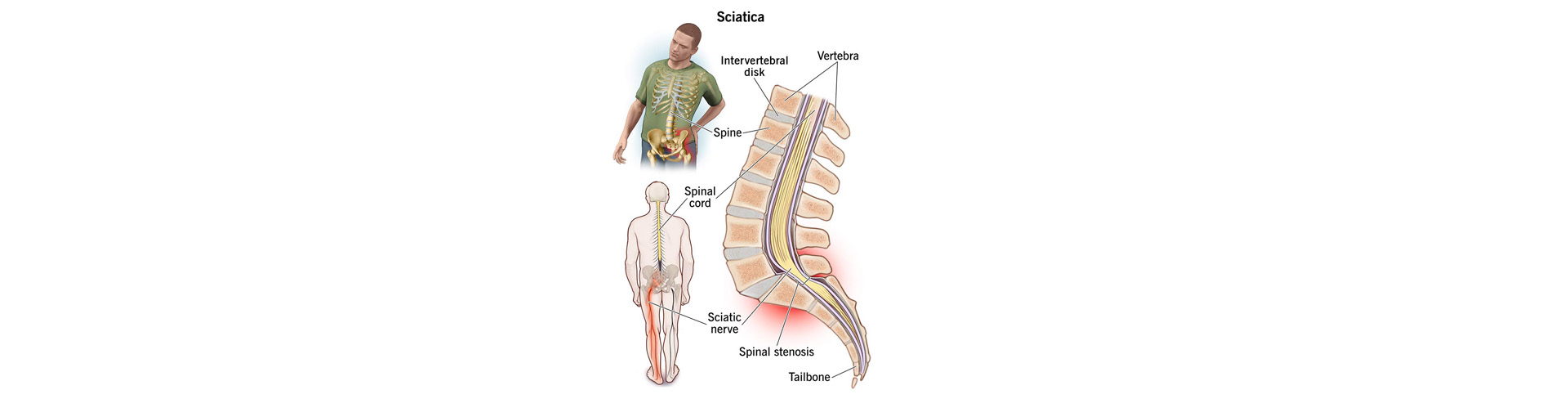
Sciatica is a specific type of low back pain that is accompanied by pain along the back surface of the lower limb and can reach the fingers or the sole of the foot. Anything that irritates this nerve can cause pain, ranging from mild to severe. Sciatica is usually caused by a compressed nerve in the lumbar spine. Sciatica is not related to the hip as many people think. Often, the term "sciatica" is confused with the more familiar term "low back pain". However, sciatica is not limited to the back. The sciatic nerve is the longest and largest nerve in the human body. It originates from the lower lumbar spine and continues through the buttocks posteriorly to the thigh and branches to the gastrocnemius (calf) down to the feet and toes. Some of the causes can be lumbar spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, tumors within the spine, infections, injuries.
Sciatica is classified according to the duration of symptoms into acute, lasting less than 4 weeks, subacute, lasting 4 - 12 weeks, and chronic, lasting more than 12 weeks.
Sciatica can be divided into non-specific and specific:
• Non-specific back pain in which the cause is unclear and is usually due to benign musculoskeletal problems (muscle or soft tissue sprain or strain, physical loading of the spine).
• Specific is the name given to back pain due to specific pathological causes, which may be mechanical (vertebral fractures, herniated intervertebral disc, spondylolisthesis), inflammatory (rheumatoid, psoriatic, ankylosing arthritis), metabolic (osteoporosis, osteopenia), neoplastic (primary or secondary bone tumours) and psychosomatic.
Symptoms
• Pain: Pain can range from muscle aches to a burning or stabbing sensation. Lumbago causes pain in the waist area. Sciatica causes back pain that 'radiates' to the lower limbs. The pain can be located anywhere along the sciatic nerve from the waist, buttocks and back along the lower limbs to the legs.
• Pain in the back, in the knee or when sitting.
• Burning or tingling in the leg.
• Weakness, numbness or difficulty in moving.
• Constant pain on one side of the back.
The clinical examination, history and various special tests and reflexes give a good picture to the orthopedist of the extent of the problem. But this is confirmed by imaging tests (X-rays, MRI).
Treatment
Conservative Treatment
Most cases of acute low back pain are satisfactorily treated with conservative treatment and measures, which include:
• Rest and relaxation.
• Medication: paracetamol, non-solid anti-inflammatories, muscle relaxants, mild opioids (tramadol, tapetanthol).
• Exercises such as walking or light stretching when symptoms are moderated and are milder.
• Hot or cold compresses that can help reduce pain. It is often useful to alternate between them and depending on the patient's response (some respond better to hot and others to cold).
• Physiotherapy.
• Epidural injection of corticosteroids in more difficult cases.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is indicated when conservative treatment fails or when the patient develops progressive functional limitation or neurological symptoms usually associated with severe disc herniation and pressure on the spinal cord. Depending on the picture and the cause also intradiscal treatments, correction of spondylolisthesis and realignment of the spine, spinal fusion are performed.
Contact the doctor to book your appointment!
The doctor will be happy to evaluate your case and recommend the optimal treatment!

