Osteochondral Lesions
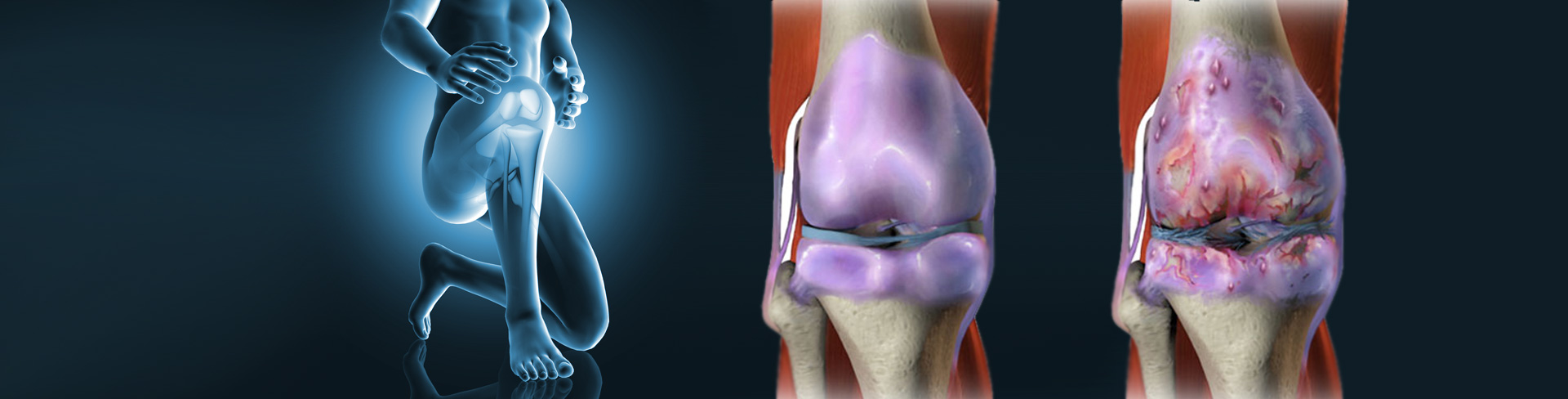
Articular cartilage is a smooth, white, soft tissue that coats the articular surfaces of the bones and allows smooth rolling between them, thus allowing smooth and painless movement in the joint. It covers the movement surface of joints, such as the knee and the ankle. Cartilage effectively helps reduce friction and also absorbs shock during movement and exercise.
By "cartilage damage" we mean the wear and tear of cartilage. The mechanism of injury includes acute and violent injury to the articular surface and/or repetitive micro-injuries. These result in the crushing or even detachment of part of the articular cartilage. In some cases, the injury may also occur due to the presence of bone cysts.
This deterioration of the articular cartilage can occur:
• After an injury (at the same time as ligament tears, meniscus tears or bone fractures).
• As a result of progressive degeneration (due to age, autoimmune diseases, genetic predisposing factors).
• From unknown-idiopathic causes (dissociative osteochondritis).
Articular cartilage (as well as nerve tissue) are the only two tissues in the human body which, once destroyed, cannot regenerate and any damage caused to cartilage is irreversible and progressively worsens.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a cartilage lesion involving the cartilage and underlying bone include:
• Pain.
• Swelling and swelling (fluid in the joint).
• Instability of the knee joint.
• Reduced range of motion, cramping and blocking of movement.
• Tenderness, often felt in the centre of the knee.
• Inability to fully extend or bend the knee joint.
The clinical diagnosis is confirmed by imaging (MRI) and radiological examination (X-Ray).
Treatment
Conservative treatment
The treatment is primarily conservative by unloading the joint using bacteria. At the same time, pharmaceutical anti-inflammatory, analgesic and debridement treatment is followed. This may be followed by physiotherapy and kinesitherapy to strengthen and restore joint movement.
Hyaluronate and chondroitin supplements are also used to strengthen the articular surface. These supplements are taken either orally or intra-articularly. Glucosamine and chondroitin are substances naturally present in the human body.
New biological techniques such as injections are also used:
• Stem Cells or Autologous Chondrocytes.
• Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP).
These have a healing effect and symptomatic relief.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is used when conservative measures do not work and the symptoms persist. In most cases of rehabilitation techniques, surgery is performed arthroscopically.
During arthroscopic surgery, techniques such as:
• Microfracture technique which is indicated for small lesions.
• Mosaicplasty, which is indicated for largerosteochondral lesions.
• Autologous chondrocyte transplantation.
Arthroscopy of the affected joint is the most painless and bloodless surgical method of choice. Through two very small incisions, each measuring 5 mm, a very high-resolution (UHD) micro-camera and specially designed micro-tools are inserted into the knee. In this way, without pain or blood loss, the surgery is performed almost percutaneously. It takes 30 - 45 minutes on average and the patient can be discharged from the clinic 3 hours after the surgery.
Contact the doctor to book your appointment!
The doctor will be happy to evaluate your case and recommend the optimal treatment!

