Degenerative Osteoarthritis
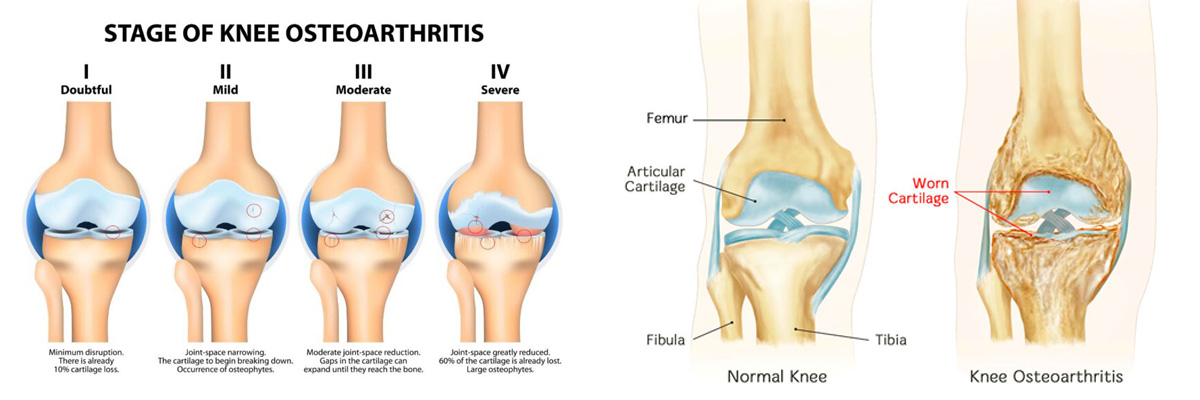
Osteoarthritis is a common form of arthritis that often affects the knee. In the first stage, the symptoms are mild, but by the fourth, the patient may need surgery. Knee osteoarthritis affects the bones, cartilage and synovial membrane of the knee. Cartilage is a slippery tissue that provides a smooth surface for joint movement and acts as a cushion between the bones. The synovial membrane is soft and aligns the joints. It produces synovial fluid for lubrication and provides nutrients and oxygen to the cartilage. As these functions cease, they no longer protect the bones of the knee joint and bone damage occurs. Knee osteoarthritis can cause pain and stiffness. Symptoms worsen over time. Age is the most common cause of knee osteoarthritis. Almost everyone will develop some degree of osteoarthritis, as the ability of cartilage to heal decreases as a person ages.
Also other factors may include:
• Weight & gender: Weight causes pressure on all joints, especially the knees in all of them. Women aged 55 and older are more likely than men to develop osteoarthritis in the knee.
• Inheritance with genetic mutations that may make a person more likely to develop knee osteoarthritis.
• Repeated injuries due to work or sports that put a strain on the joints.
• Other diseases. People with rheumatoid arthritis, the second most common type of arthritis, are also more likely to develop osteoarthritis. People with certain metabolic disorders, such as iron overload or too much growth hormone, are also at greater risk of osteoarthritis.
Symptoms
• In the initial stages of the disease, pain is manifested, mainly during loading of the joint that occurs after rest, while progressively as the disease progresses the pain becomes constant, troubles the patient during night sleep and leads to a significant limitation of daily activities, with difficulty in movement.
• Oedema (swelling) and burning sensation in the joint.
• Stiffness especially in the morning or when sitting for a while and redness.
• Twitching, "breaking" sound during movement.
• In the final stages there is atrophy of the muscles around the knee area.
Treatment
Conservative Treatment
The primary goals of treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee are pain relief and return of mobility. Patients with mild symptoms are recommended pain relief modalities such as:
• Mild analgesics - anti-inflammatory
• Weight reduction
• Modification of daily activities
• Physiotherapy for muscle strengthening
• Use of a walking stick to help with walking
• Injection treatments in the knee joint (Hyaluronic acid - PRP)
Alternative treatments: Some alternative treatments that may be effective include topical creams with capsaicin, acupuncture or various supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin.
Surgical Treatment
When other treatments are not enough, surgery is considered. The decision of the need for surgery is made together with the patient and not based on x-rays alone. The operation of changing the worn cartilage and the bone underneath it is called "total knee arthroplasty". During this procedure, the worn articular surfaces are replaced with a prosthesis made of durable metal materials.
Total knee arthroplasty remains a serious procedure that is performed as planned and with proper patient preparation. But with the help of improved and less traumatic surgical techniques (non-traumatic or minimally invasive techniques) and advances in the orthopaedic materials and prostheses we use, recovery and return to daily activities is faster than before.
Surgical techniques of knee arthroplasty are performed with smaller incisions and especially without injury to the muscles of the area (the quadriceps femoris). This benefits the patient in faster mobilization and walking after surgery.
The hospitalization of the patient for total knee arthroplasty is usually of the duration of a few (3-4) days. Already during hospitalization the patient is mobilized and encouraged to walk immediately and on the1st postoperative day with the use of a walker.
Contact the doctor to book your appointment!
The doctor will be happy to evaluate your case and recommend the optimal treatment!

