
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by reduced bone density resulting in deterioration of bone architecture, reduced mechanical strength of the bones and increased risk of fracture. It is also known as a "silent disease" because it often progresses without obvious symptoms until a fracture occurs. The causes of the reduction in bone density and loss of bone mineral content are due to the creation of a negative bone balance, i.e. the mismatch between the rate of formation of new bone and the degradation of old bone. This has the unfortunate consequence of causing bone fractures even with minimal stress, such as lifting light weights, and cases have been observed where fractures occur in the absence of an external factor. The sites considered most susceptible and exposed to fractures in osteoporosis are the vertebrae, wrists and the head of the femur.
Osteoporosis can affect people of any age, but it is most common in:
• Women after menopause due to a decrease in estrogen.
• Women after menopause after menopause after menopause due to the reduction of menopause.
• People with: Family history of osteoporosis, low calcium and vitamin D intake, sedentary lifestyle or lack of exercise, smoking habit or excessive alcohol consumption, hormonal disorders (e.g. hypogonadism, hyperthyroidism), long-term use of corticosteroids.
Osteoporosis is divided into primary and secondary osteoporosis.
Primary osteoporosis
• The most common type of primary osteoporosis is called postmenopausal osteoporosis, which occurs when women stop releasing estrogen after menopause.
• Senile osteoporosis occurs in men and women over the age of 70.
• Idiopathic osteoporosis (rare) at a young age.
Secondary osteoporosis
Secondary osteoporosis results from the presence of specific diseases - either the diseases themselves or the chronic specific medication to treat them. Indicatively:
• Diabetes mellitus.
• Endocrine diseases (hyperparathyroidism, hyperthyroidism).
• Rheumatoid arthritis.
• Gastrointestinal diseases (Crohn's disease, celiac disease, chronic liver disease).
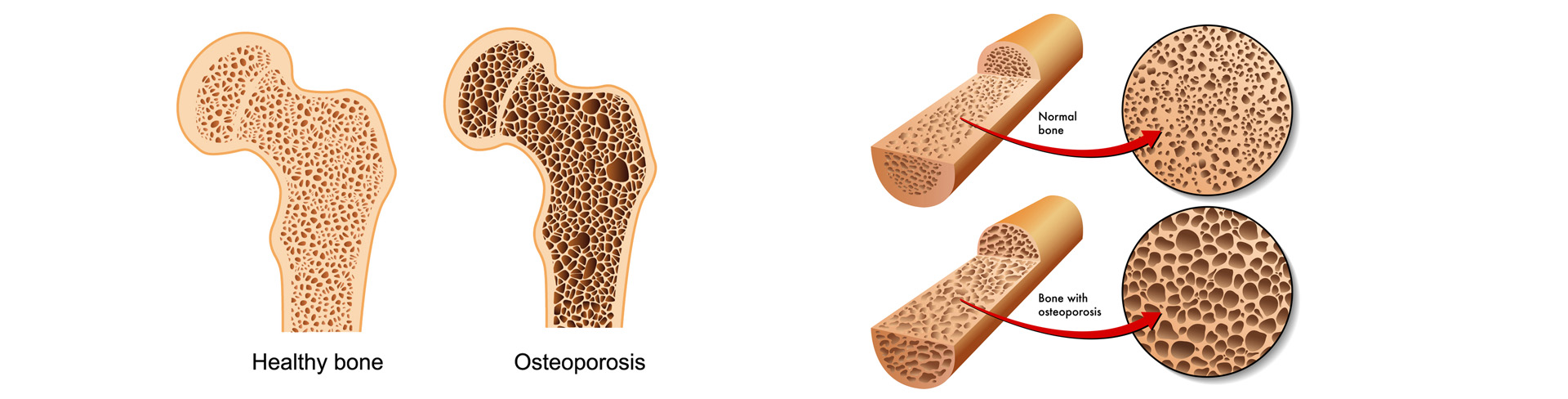
Symptoms
Osteoporosis often causes no symptoms in the early stages. When the condition progresses, they may appear:
• Pain in the back or spine.
• Sedimentation of height (due to fractures in the vertebrae).
• Fracture after a minor fall or injury (e.g. hip, wrist, vertebrae).
• Difficulty balancing when standing or climbing stairs.
The diagnosis is made by measuring bone density through special tests, such as:
• DEXA (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry), which measures the density in the hips and spine.
• Blood tests to evaluate bone metabolism.
Treatment
Conservative Treatment
• Pharmaceutical treatment:
- Bisphosphonates (e.g. alendronate, risedronate).
- Hormonal treatments for post-menopausal women.
- Parathyroid hormone analogues and other newer treatments.
- Analgesics (paracetamol, codeine, rarely morphine).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, naproxen, etc.)
- Calcitonin and teriparatide (indicated for pelvic and spinal fractures).
• Supplements: Calcium and vitamin D.
• Special physiotherapy to improve balance and prevent falls.
• Food adaptation.
• Thoracolumbarsplints and guardians (may help prevent further compression of the vertebral bodies).
Surgical Treatment
Open surgical treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures is rarely indicated. It concerns cases with neurological semiology and significant skeletal instability.
Unfortunately, the poor bone density that characterizes the vertebrae makes stabilization and arthrodesis of these vertebrae quite difficult.For pain management, the application of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty is extremely effective and safe. They consist of injecting a special material (PMMA = bone cement) into the pathological vertebrae, with the aim of restoring the normal height and strength of the bone.
Contact the doctor to book your appointment!
The doctor will be happy to evaluate your case and recommend the optimal treatment!

