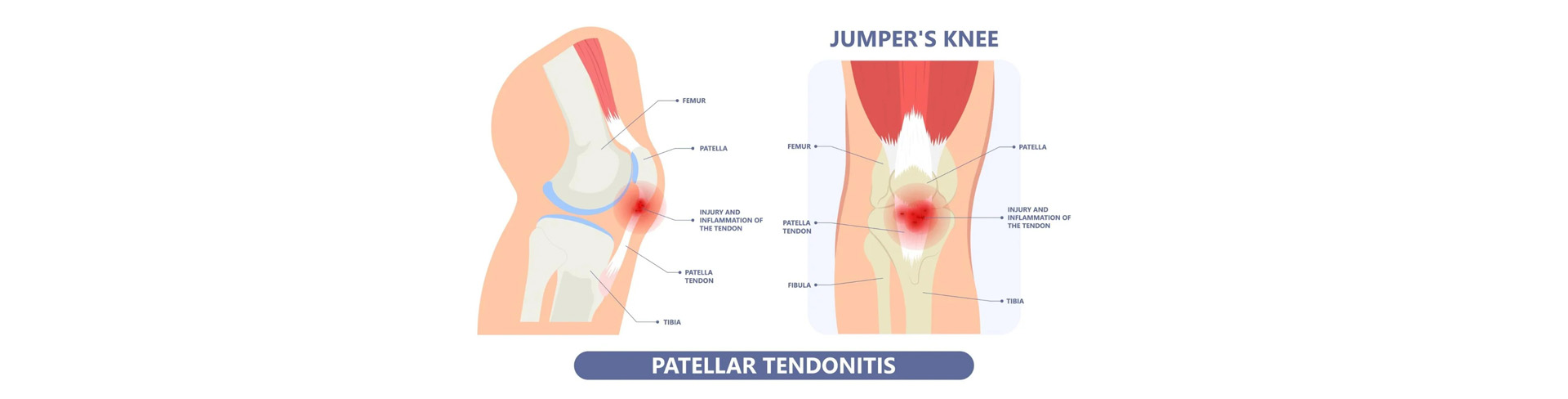
Patellar Tendinitis
The patellar tendon connects the patella to the tibia and is the end of the quadriceps muscle. Patellar tendinitis is the inflammation of the tendon that connects the patella to the tibia. The condition is also known as patellar tendinopathy or knee tendinopathy. Inflammation of the tendon leads to pain and limited mobility and is usually the result of injury or overuse.
It usually occurs in track and field, football, basketball or volleyball athletes. Furthermore, the condition can occur in people who are not athletes but climb many stairs in their daily lives repeatedly and generally when minor injuries and knee strain are repeatedly sustained. Jumper's knee can occur more easily in patients who have problems with proper alignment of either the hips or knees and limbs.
Symptoms
Symptoms may vary in severity depending on the extent of the injury. Common symptoms include:
• Pain and tenderness in the front of the knee, near the kneecap.
• Swelling and inflammation around the patellar tendon.
• Stiffness and limited mobility in the knee joint, especially after periods of inactivity.
• Creaking sensation and clicking sound when bending or straightening the knee.
• Pain aggravated by activities involving jumping or bending the knee.
• Increased pain at night.
• Pain that improves with rest but may return after resuming activity.
The diagnosis of jumper's knee is made through ultrasound and MRI.
If left untreated, patellar tendinitis can lead to a chronic condition that can affect the ability to participate in sports and other activities.
Treatment
Conservative Treatment
Jumper's knee is treated conservatively in about 80 - 90% of cases. The orthopaedic doctor after diagnosing the case recommends, among other things:
• Rest.
• Ice therapy (especially after activity).
• Reduction of activity that puts a strain on the knee.
• Use of a special splint.
• Appropriate medication , Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
• Physiotherapy.
• Local injection of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) if symptoms persist.
Surgical Treatment
Non-conservative treatment is chosen in cases where symptoms are severe and persistent or in chronic forms. Thus, when the patient does not respond to the previous methods, the doctor may deem it necessary to surgically repair the tendinopathy. This option, includes arthroscopic treatment of chronic tendinitis.
Surgical treatment is also necessary if the patellar tendon is severed (ruptured patellar tendon). In this case, stitching can only be performed surgically.
Contact the doctor to book your appointment!
The doctor will be happy to evaluate your case and recommend the optimal treatment!

